Syslog
| Done |
|---|
It is an industry standard for logging messages related to events that happened in the device. This is an important feature to diagnose and pinpoint issues.
Theses messages can essentially be stored in two ways:
- RAM
- Syslog Server
Syslog Message Format
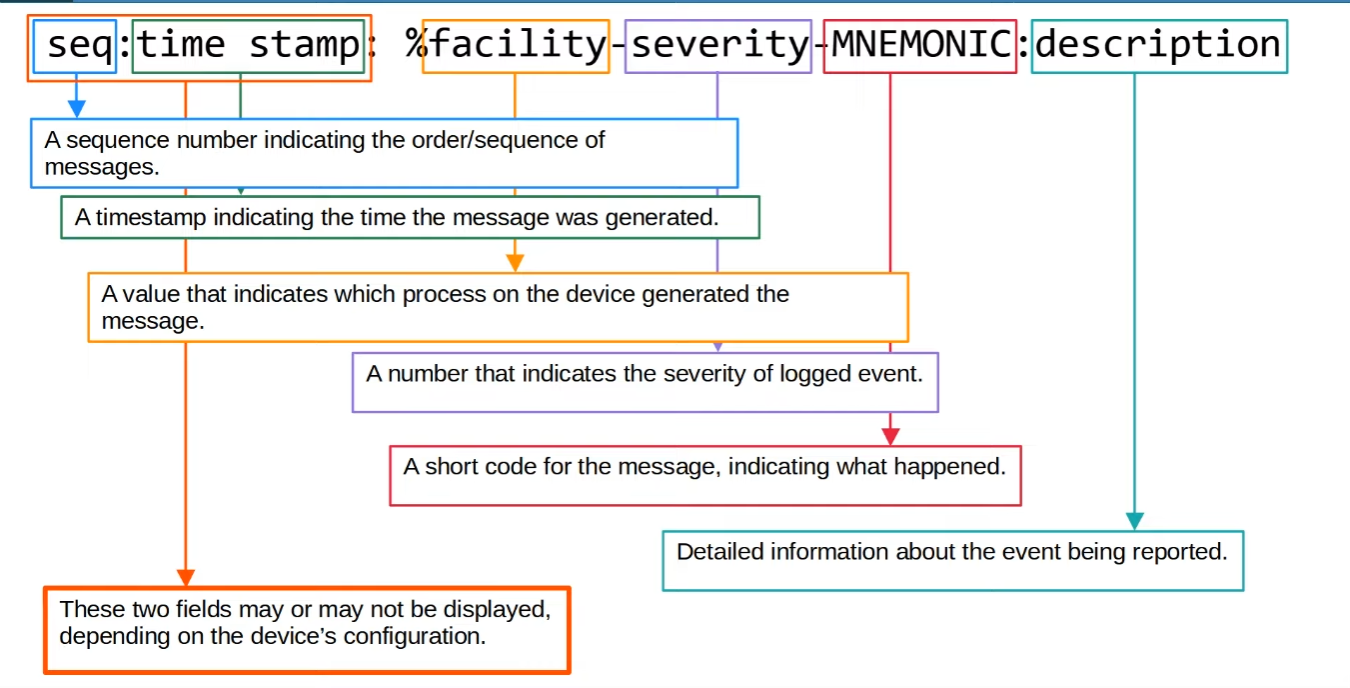
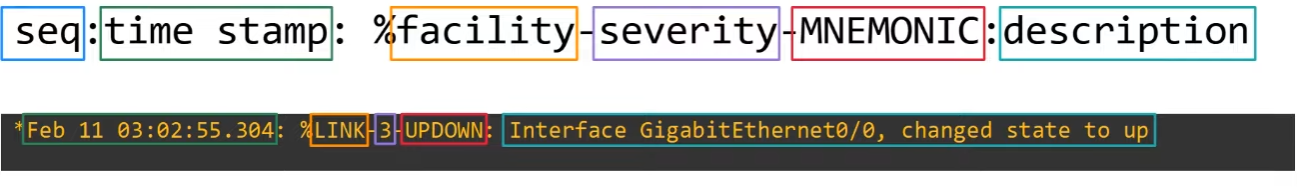
Severity Levels
| 0 | Emergency |
| 1 | Alert |
| 2 | Critical |
| 3 | Error |
| 4 | Warning |
| 5 | Notification |
| 6 | Informational |
| 7 | Debbuging |
💡
NOTE: Every Awesome Cisco Engineer Will Need Ice cream Daily
Logging Locations
- Console → CLI
- All messages enabled by default
- VTY → SSH/Telnet
- Messages disabled by default
- Buffer → RAM
- show logging
- External server → UDP 514
Configuration
Console
configure terminal
logging console {level}VTY
configure terminal
logging monitor {level}
exit
terminal monitor🚨
IMPORTANT: To display the Syslog messages with SSH/Telnet, terminal monitor command must issued every time you log in.
Buffer
configure terminal
logging buffered {size-MB} {level}External Server
configure terminal
logging [host] {ip-address} // Points to the Syslog Server
logging trap {level} // Selects the level to which send syslog messages💡
NOTE: The level can be either its name or its number. Also, if you inform a level, it will consider also all its higher levels. For example, if you put 6 in the command, the IOS will send syslog message of levels 0 - 6.
Additional
#1
If you don`t want to receive a syslog message while typing in the CLI, issue the command:
line console 0 //This is the console line in this example
logging synchronous#2 Enable/Disable Time stamp
configure terminal
[no] service timestamps log [datetime | uptime]#3 Enable/Disable Sequence
configure terminal
[no] service sequence-numbers