Routing Fundamentals
| Done |
|---|
Routing
It is the process the routers use to choose the path IP packets should take over a network to reach its destination.
Routers store all known destinations to its routing table.
When routers receive packets, they check their routing table to choose the best path to forward an IP packet.
The Routing Table is populated by 2 methods:
- Dynamic Routing: It happens when a routing protocol, such as OSPF, share the known destinations of a routers with a neighbor one, all of them simultaneously, so each one fills the other’s routing table.
- Static Routing: It is the manual way. In this method, an engineer/technician has to manually configure the route.
Route
It tells the router that to reach a Destination X, it should forward the packet to the next-hop Y or If the destination is connected directly to it or if it is intended for it, send to itself.
Automatically added routes
After assigning an IP Address and enabling an interface, 2 types of routes are added:
- Local (L):
- It is the assigned IP to that interface, 192.168.1.1 for example. Notice that the netmask is switched to /32
- Connected (C):
- It represents the network address, 192.168.1.0 for example. Notice that the netmask stays at the used prefix length
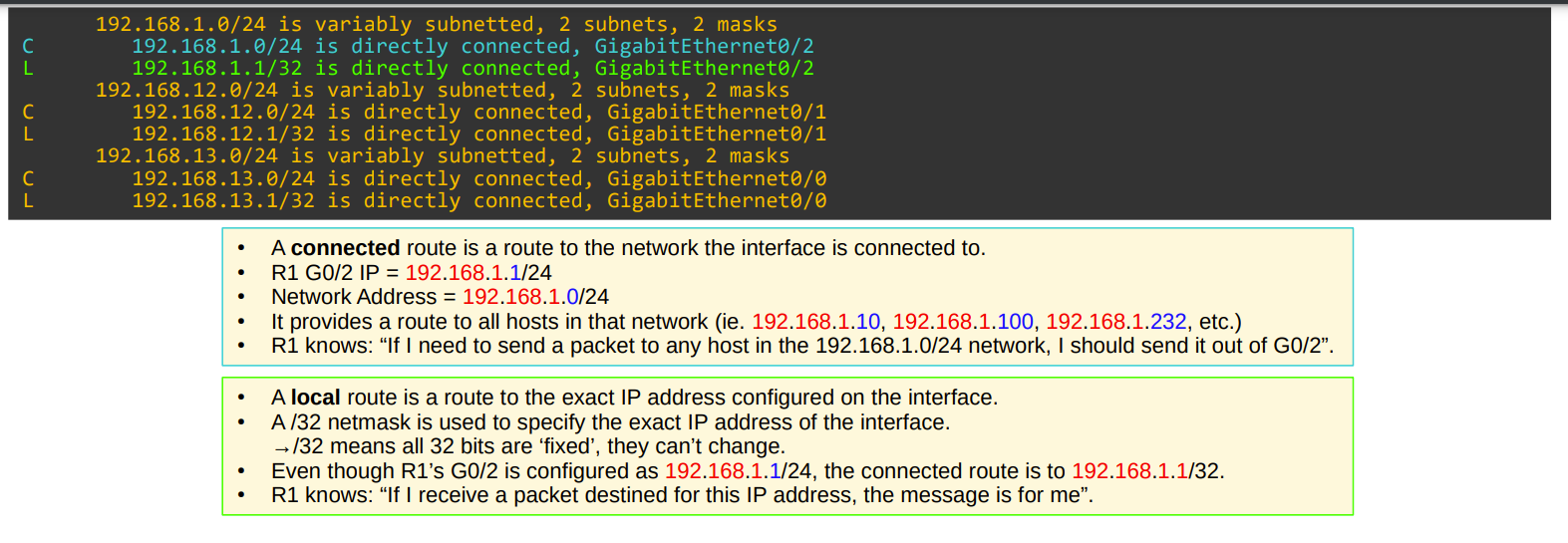
A router will choose the most specific address in order to select a route. For example, if it receives a packet for 192.168.1.1, It will forward the packet to the local rather than the connected one, because 1 is more specific than 256.
- If the router receives a packet with a destination IP Address to networking with no matching route, it will drop the packet.
- If there is multiple routes, the router will choose the most specific

Static Routing
When a endhost needs to send a package outside its network (LAN), it forward it to the default gateway.
Set Static Route
Option #1 - Next-Hop IP Address
configure terminal // Global Config Mode
ip route 192.168.15.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.45.4 //ip route {ip-address} {netmask} {nexthop}Option #2 - Interface
configure terminal // Global Configuration Mode
ip route 192.168.15.0 255.255.255.0 g0/1//ip address {ip-address} {netmask} {exit-interface}Option #3 - Both
configure terminal // Global Configuration Mode
ip route 192.168.15.0 255.255.255.0 g0/1 192.168.45.4 //ip address {ip-address} {netmask} {exit-interface} {next-hop}Default Route (Default Gateway)
If a packet has a destination’s IP address that matches no routes in the routing table, it will forward the packet to the next-hop specified.
configure terminal // Global Configuration Mode
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.50.3 //ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 {next-hop}Filter search in running-config
show running-config | include ip route //show {file} | include {term}