RIP & EIGRP
| Done |
|---|
RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
- It uses Distance Vector algorithm (”routing by rumor”)
- The metric is Hop Count
- The maximum hop count is 15, anything greater than that will be unreachable
- Has three versions:
- RIPv1 and RIPv2, which use IPv4
- RIPng (RIP Next Generation), which uses IPv6
- There is two types of messages:
- Request: Ask the neighbor router to send its routing table
- Response: Sends its routing table to the neighbor device
- RIP-enabled devices send messages every 30 seconds
RIPv1 vs RIPv2
RIPv1:
- Only advertises classful addresses
- Doesn`t support VLSM, CIDR
- Doesn`t include subnet masks in the messages, it assumes the subnet mask of a neighbor router by the first octet (classful)
- Messages are sent via Broadcast
RIPv2:
- Supports VLSM, CIDR
- Advertises the subnet mask of the destination addresses of its routing table
- Advertises via Multicast 224.0.0.9
Configuration
Enter RIP configuration mode
configure terminal
router ripSelect the RIP version
version 2 // In RIP configuration modeDisable Auto-summary
This function saves bites in the wire by not sending the mask
no auto-summary // In RIP configuration modeSpecify which networks advertise
This command specifies which interface it will activate RIP and also what networks it will advertise
network {subnet ID} // In RIP configuration modeDisable RIP messages on an interface
passive-interface {interface} // IN RIP CONFIGURATION MODEShare the same default route
default-information originate // In RIP configuration modeChange the number of maximum similar paths in the routing table
maximum-paths {1-32} // In RIP configuration modeChange de Administrative Distance
distance {value} // In RIP configuration modeEIGRP
It was Cisco`s Proprietary routing protocol, however Cisco`s published it openly so other vendors could implement it. But, it is still not widely used, being still considered Cisco`s protocol.
- Is is considered an advanced Distance Vector routing protocol.
- It is much faster than RIP in reacting to changes
- It doesn`t have a hop count limit of 15
- Sends messages to the multicast address 224.0.0.10 (1 more than RIPv2)
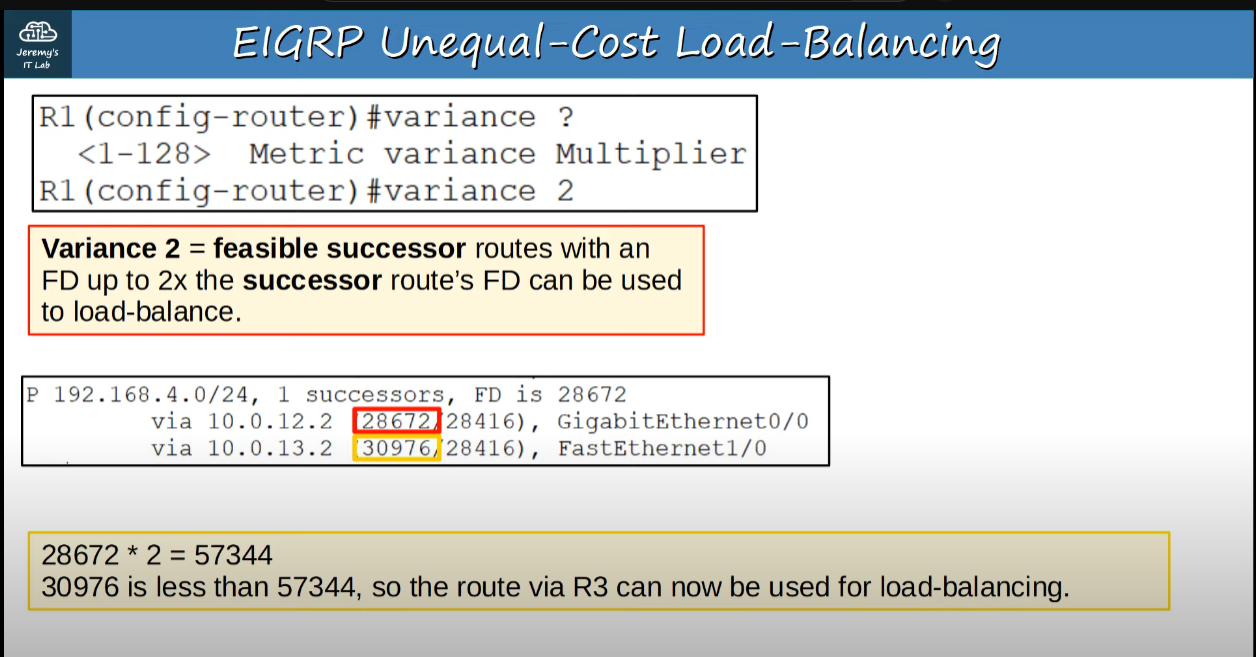
- Is the only IGP that can perform unequal-cost load-balancing (by default it performs ECMP over 4 paths like RIP). In other words, it can send load-balance traffic between links that have different costs.
Enter EIGRP Configuration mode
configure terminal
router eigrp {as value}Disable Auto-Summary
It is the same as RIP, which advertises and assumes only classful IP Addresses are used, so you better disable it.
router eigrp 1
no auto-summaryNetwork command
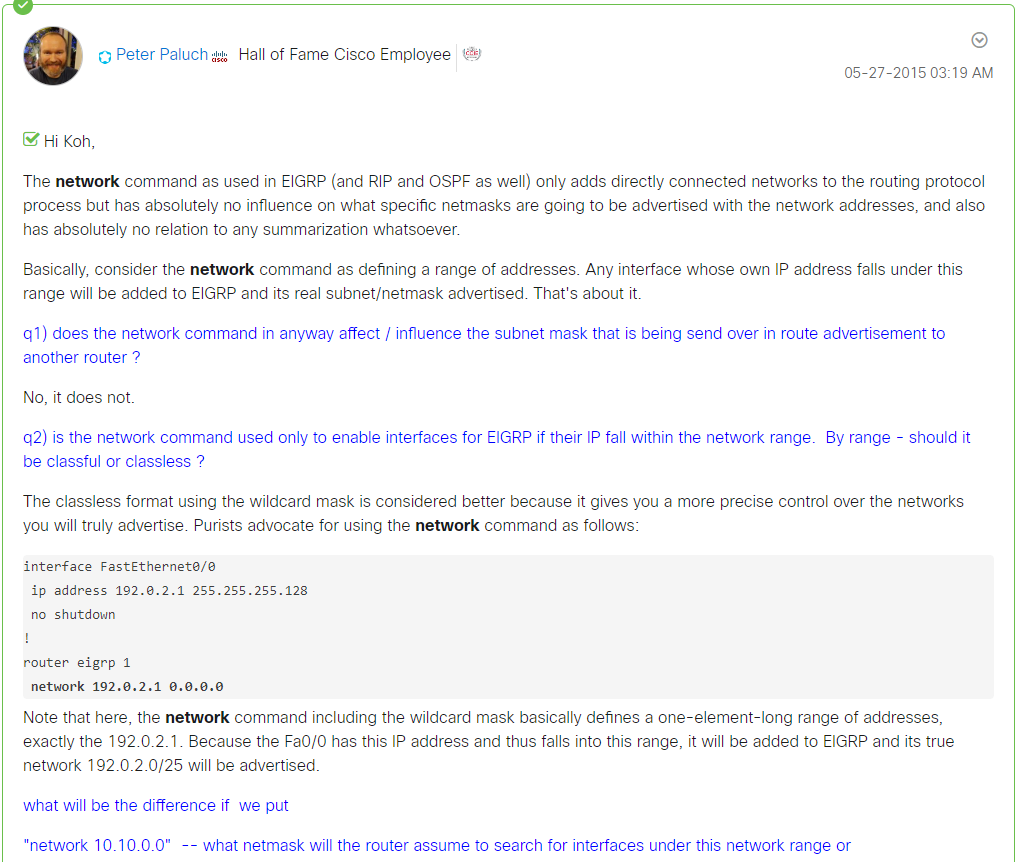
It works the same as in RIP and OSPF. It will specify the range of IP Addresses, and any interface in that range will both send EIGRP messages and will advertise their subnet/network.
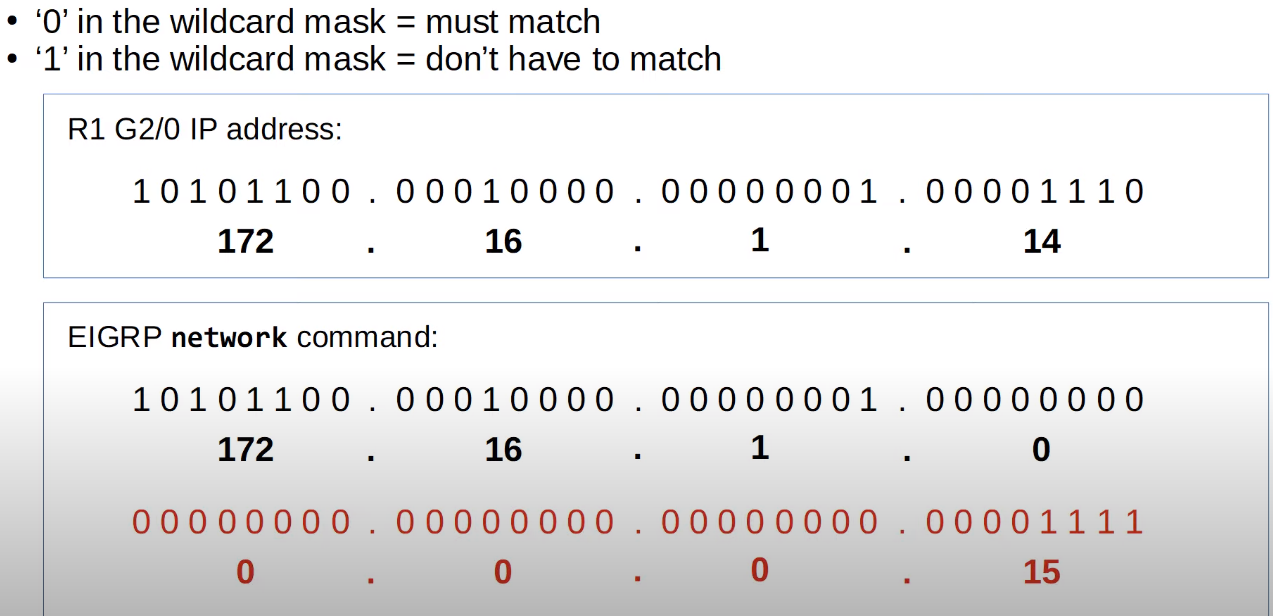
However, you can use a WILDMASK here (The inverse of a subnet mask), to specify only that range of ip address instead of a range which defaults to the classful rules of /8, /16 and /24.

configure terminal
router eigrp 1
no auto-summary
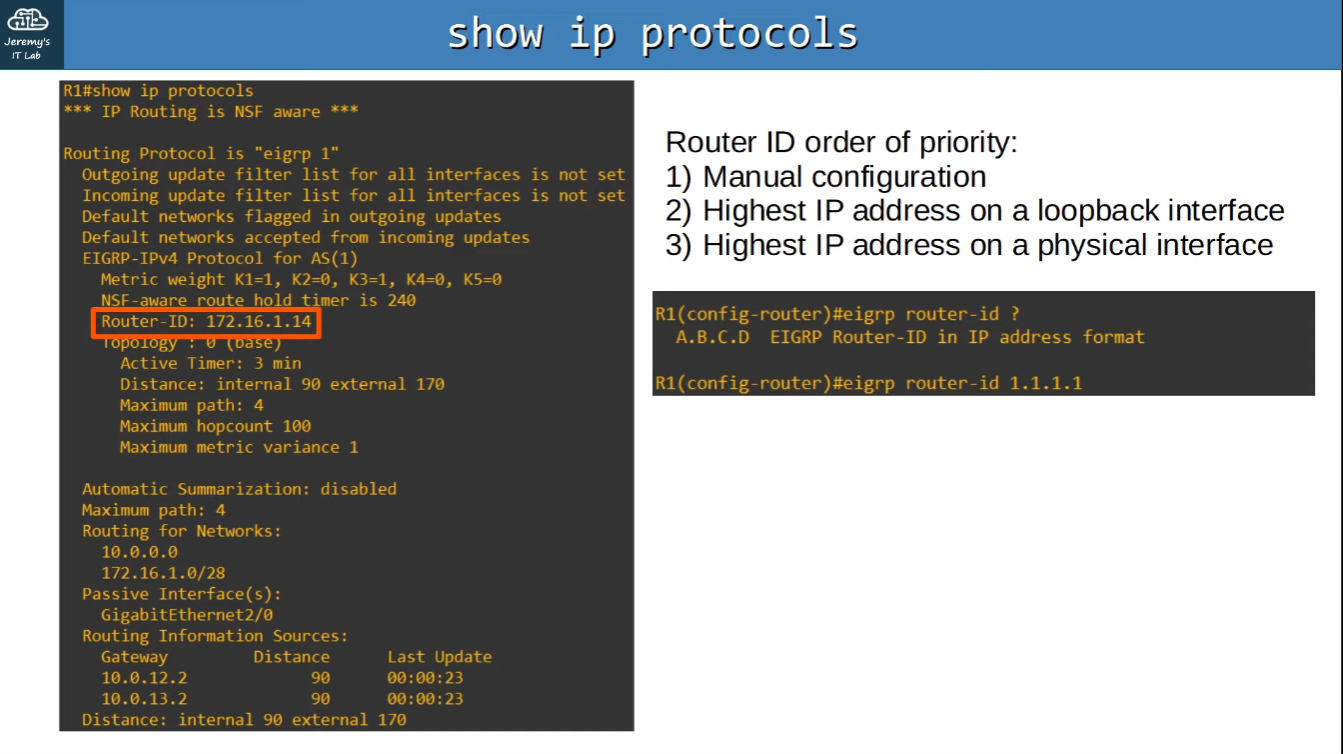
network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255Each router in a EIGRP Autonomous System will have a unique Router ID which can be defined as followed:
- Manual Configuration (eigrp router-id value)
- Highest IP Address on a loopback interface (Router`s virtual interface)
- Highest IP Address on a physical interface
See EIGRP Neighbors - Adjancies
show ip eigrp neighborsSee all the routes advertised (including the ones that were not selected)
show ip eigrp topologyTerminology
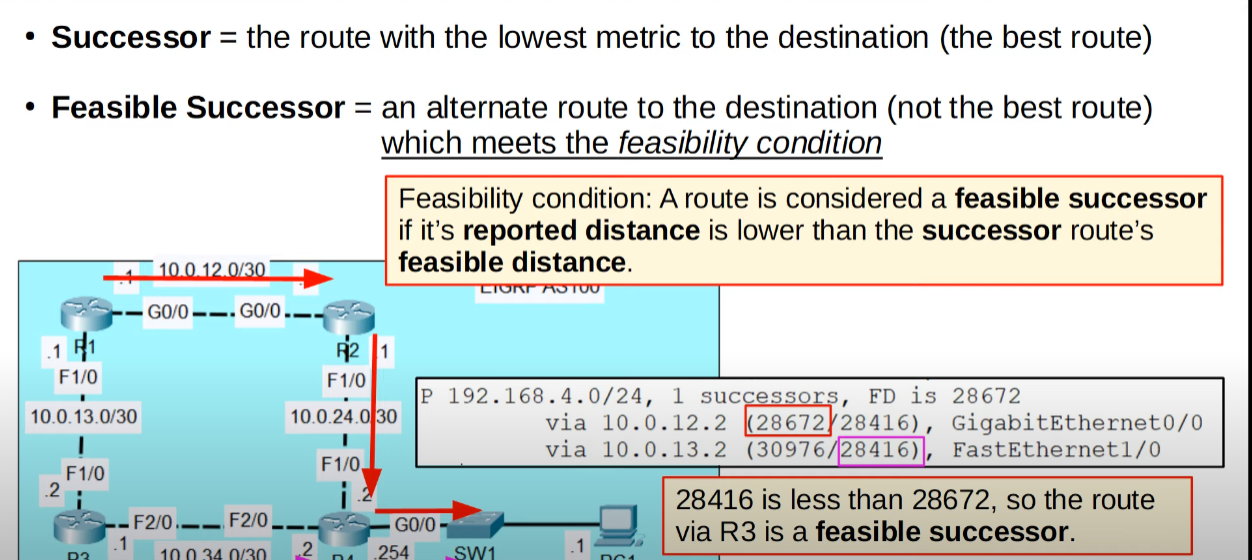
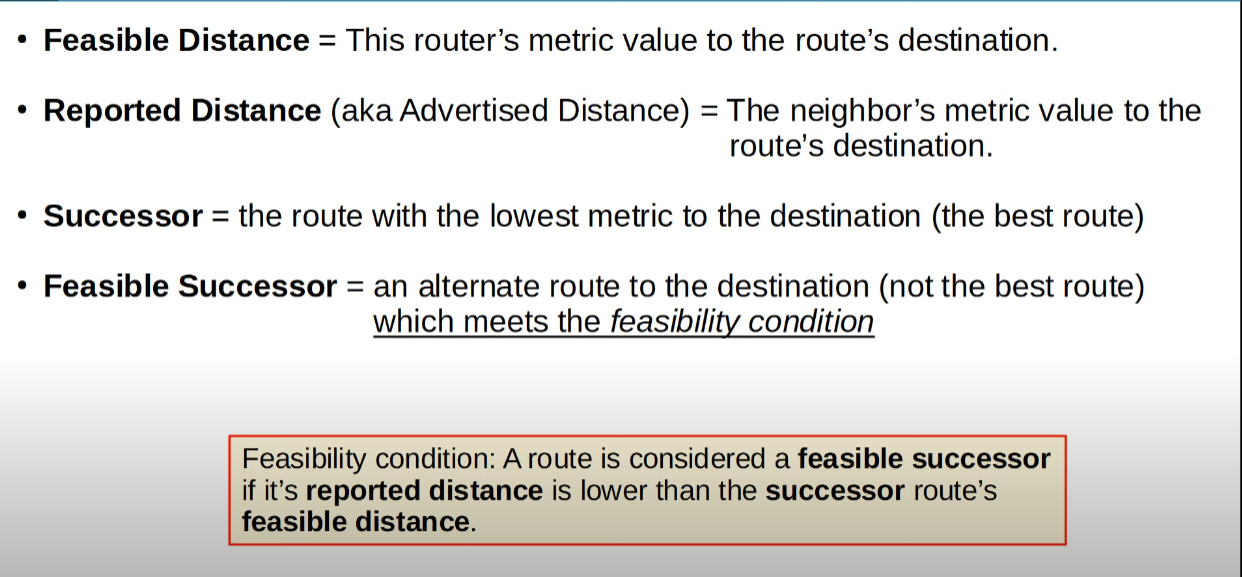
- Feasible Distance: This router`s metric value to the route`s destination
- Reported Distance (Advertised Distance): The neighbor`s metric value to the route`s destination (Basically, the neighbor`s feasible distance)
- Successor: Best candidate to route in the routing table, the one with the lowest metric
- Feasible Sucessor: It a alternate route to the destination (not the best route). It must meet the feasibility condition: its reported distance must be lower than the successor’s feasible distance
Unequal-Cost Load-Balancing