IPv4 Address
| Done |
|---|
Address
It is 32 bits (4 bytes) long
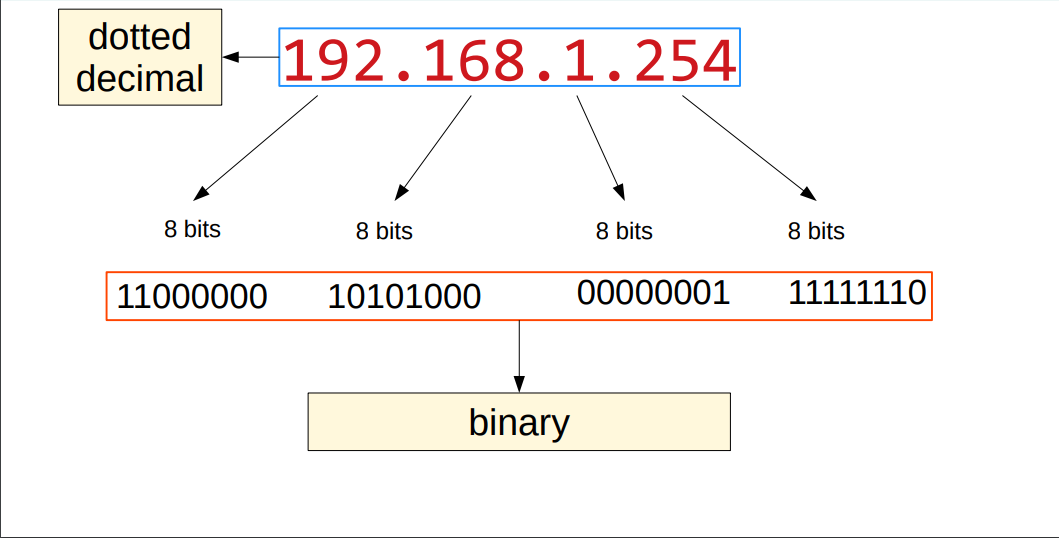
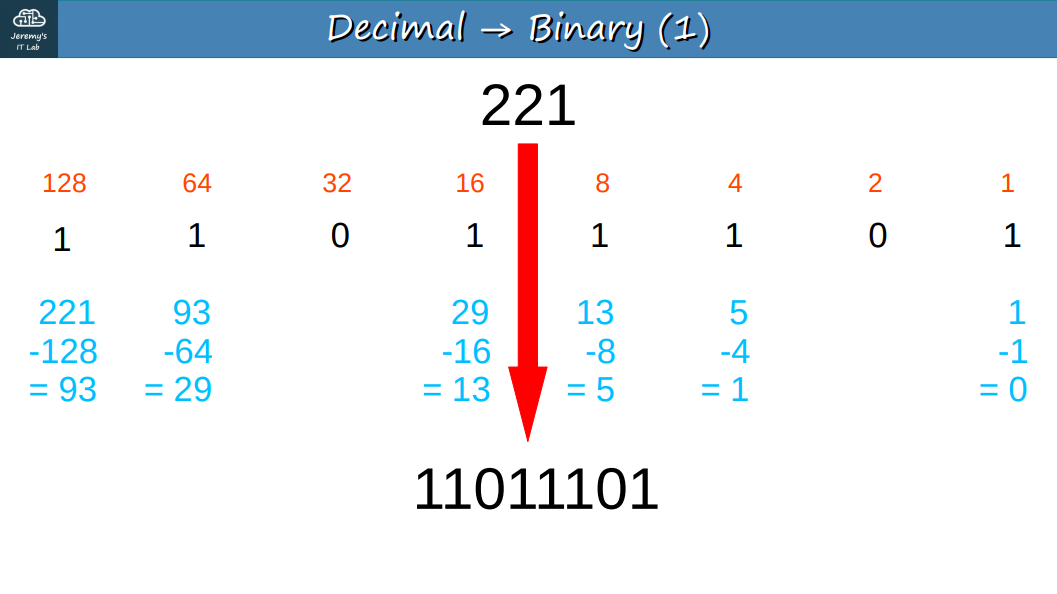
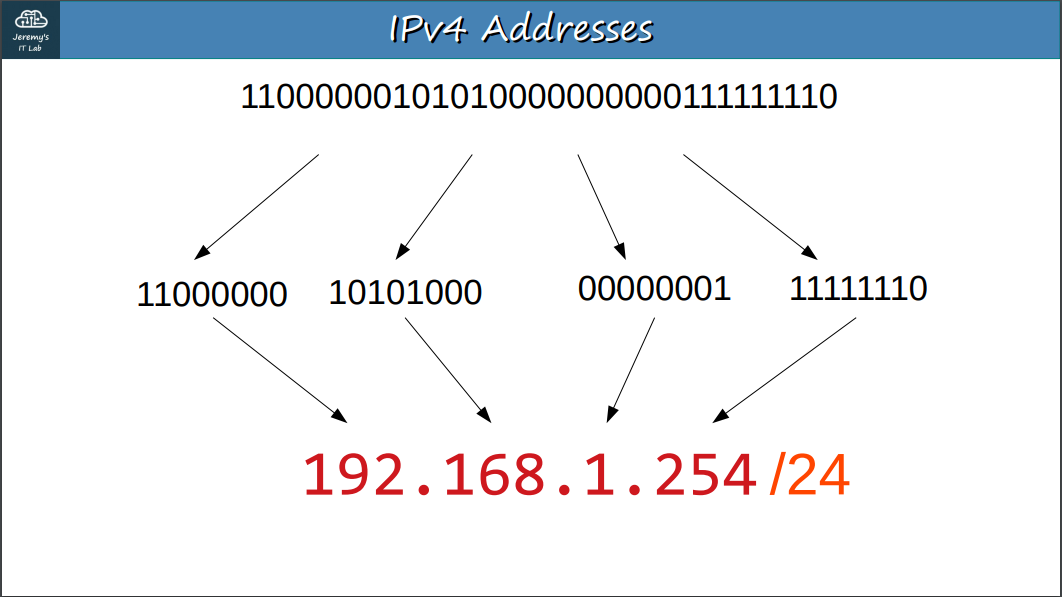
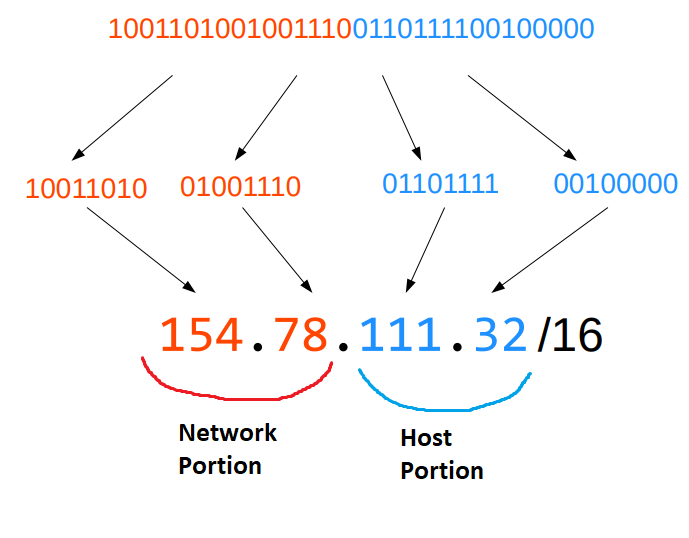
The “/” after the IP Address, for example: 192.168.0.1/24, says that from left to right: 24 bits represent the Network portion and 8 bits (the rest) represent the Host portion. The Network portion can count how many networks can be created and the Host portion how many clients can have their own IP Address
Classes
| Class | First octet | First Octet range | Prefix Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0xxxxxxx | 0-127 | /8 |
| B | 10xxxxxx | 128-191 | /16 |
| C | 110xxxxx | 192-223 | /24 |
| D | 1110xxxx | 224-239 | |
| E | 1111xxxx | 240-255 |
Class D is for Multicast Address and Class E is reserved for experiments.
Net mask
It is the same as the prefix length, but it uses a different representation: dotted decimals.
| Prefix Length | Net Mask |
|---|---|
| /8 | 255.0.0.0 |
| /16 | 255.255.0.0 |
| /24 | 255.255.255.0 |
Network Address
It is the first address of a network. It is identified when all the Host portions are zeros. It cannot be assigned to hosts.
Examples: 192.168.1.0 118.0.0.0 150.178.0.0
Broadcast Address
It is the last address of a network. It is defined when all hosts portions are represented by 255. It cannot be assigned to hosts.
Examples: 192.168.1.255
Router Configuration
Show interfaces
enable
show ip interface briefThis commands lists information about each interface in a router
Interfaces in full details
show interfaces descriptionshow interfaces g0/0 //show interfaces {interface-name}Description in interfaces
interface g0/0 //interface {interface-name}
description ##to SW1## //description {description}Select Interface
Option #1
configure terminal #enter Global Config Mode
interface gigabitethernet 0/0 //interface {interface-name}
Option #2
configure terminal
in g0/0Set the Interface`s IP Address
ip address 10.255.255.254 255.0.0.0 //ip address {ip-address} {subnet mask}
no shutdown //enables the interface by cancelling the shutdown command with "no"