FTP & TFTP
| Done |
|---|
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) and TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) are both industry standard protocols. They are used to transfer files over the network, however there are some differences between each one.
In Network Administration, one of the roles of this protocols, is to upgrade the image file of the IOS. You will usually have an FTP/TFTP server to copy from or to.
TFTP
The “Trivial” keyword stands for simplicity. TFTP is a lightweight version of FTP, has only ONE capability: copy file from or to a TFTP server, that`s it.
Also, it does that WITHOUT any Encryption or Authentication. So it is better fitted for a controlled environment.
It uses the UDP Port 69 to reach the server TFTP service. HOWEVER, despite the UDP protocol it DOES HAVE RELIABILITY FEATURES. It uses the “lock-step” mechanism of using timers and acknowledgments to assure the data is delivered, it does that with the messages:
- Read Request
- Data
- Ack

Connections types
- Connection: It is initiated with a “Read Request” from the client to the server, then the server establishes the connection by sending a data message or refuse it with an error message.
- Data Transfer: It is the actual transfer of data with Data and Ack messages that assure reliability to the process.
- Connection Termination: After the last Data message has been sent, the client will reply with the last Ack message, terminating the connection.
Interesting Fact
TFTP only uses the UDP Port 69 to initiate the connection, after that the Server will use a random port (TFTP Transfer Identifier (TID)) as the source and the client will start to use that port as the destination.

FTP
It is a more complete solution than TFTP. It was created before TFTP however.
It has Authentication, but no Encryption. For encryption there is the upgraded version of FTP, called FTPS (FTP over SSL/TLS) or the new protocol SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol).
It can do the following:
- Add/Remove Directories
- List the files
- Browse directories
- Copy files from and to a server
- etc.
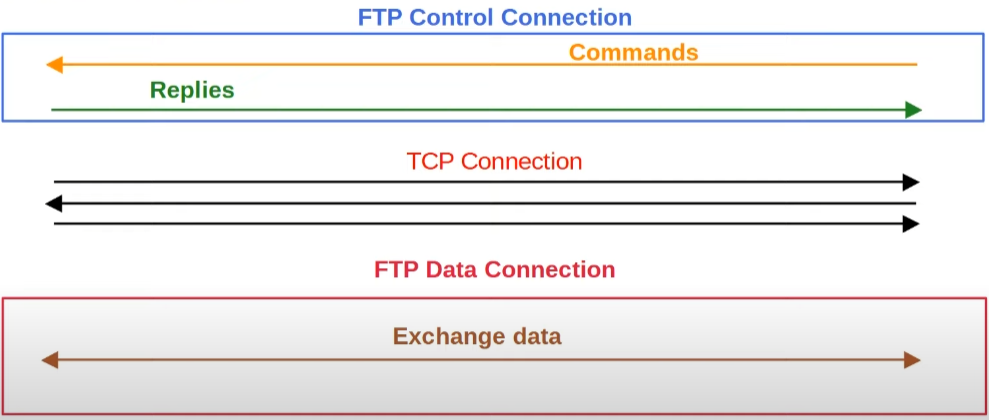
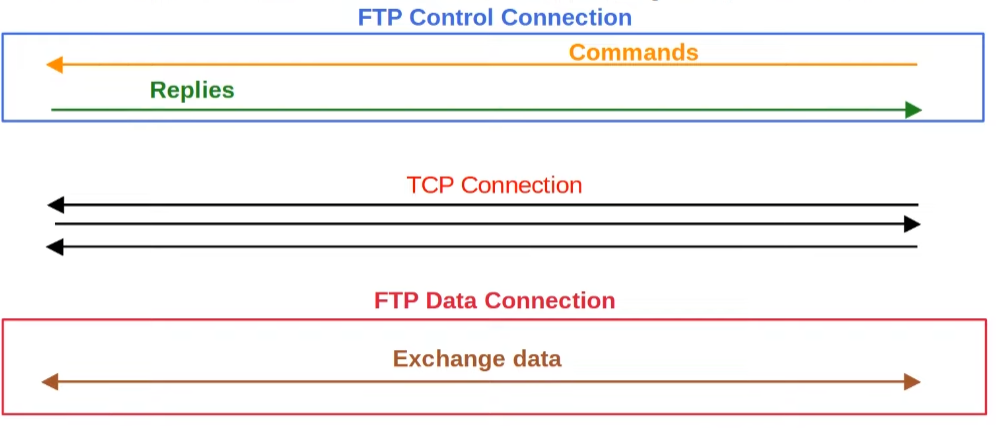
Another great difference is the fact that FTP establishes two simultaneous connections while being used:
- Control: It the first established connection with the port TCP 21 and is used only to send and receive commands.
- Data: It is the actual data exchange, created as a consequence of a command, through the port TCP 20. It can be initiated by two methods:
FTP vs TFTP
| FTP | TFTP |
|---|---|
| TCP 20 (data) and TCP 21 (control | UDP 69 |
| Multiple features (delete files, list files, browse directories, create and delete directories, copy files, etc.) | Only Copy files to or from a server |
| Authentication | NO Authentication |
| Complex | Simple |
File Systems
A file system is responsible for knowing where the data is stored and how to retrieve it. There are multiple file systems in Cisco IOS.
There are the following types of file systems:
- disk: Actual storage devices, like flash memory. It is where the IOS is stored, after boot it will be loaded into the RAM.
- opaque: Logical file systems used for internal functions
- nvram: Non-volation RAM responsible for storing the startup-config
- network: External file systems, like FTP/TFTP servers.
Show commands
List File Systems
show file systemsSee the current version of IOS
show versionSee the files in the flash memory
It can show the image of the IOS.
show flashUpgrade Cisco IOS from a TFTP/FTP Server
- Copy the file into flash
//Option#1 - TFTP copy tftp: flash: //Yes, it is done in Privileged EXEC mode //Fill the fields that will be prompted //Option#2 - FTP configure terminal ip ftp username {username} ip ftp password {password} exit copy ftp: flash: //Privileged Exec Mode
- Check if the file was indeed downloaded
show flash
- Select the file and boot from it
configure terminal boot system flash:{file-name} exit write memory reload
- Ensure that the correct file was booted
show version
- Erase the old version IOS file
show flash delete flash:{old-file-name} show flash
Resume of commands